for reference:According to statistics, one in every five adults worldwide suffers from knee osteoarthritis. Knee osteoarthritis can be unilateral or bilateral; pathologic diagnosis is twice as common in women as in men. People over the age of 45 often face the problem of joint deformation due to age-related body changes. If this diagnosis is made in a young person, the cause is usually trauma.
Why do pathological changes occur?
- Overweight – the joint must bear additional loads;
- Osteoporosis is a pathology in which bone tissue undergoes demineralization.
- Chronic diseases related to metabolic disorders in the body;
- Traumatic Sports – Due to the frequent trauma to the knee joint, knee joint disease is often referred to as a football player’s disease;
- Certain types of occupational activity related to strenuous physical activity - osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis - are found in loaders;
- Spinal injuries, in which the load distribution of the lower extremity joints is disrupted;
- Genetic predisposition.

How to recognize disease
- Morning stiffness of joints;
- Restricted movement after staying in one location for a long time;
- Discomfort in the knees when climbing stairs - burning sensation, allergies;
- Knee pain at night;
- pain after physical exertion or exercise;
- Periodic sudden weakness of the lower limbs. In the case of right-sided knee joint disease or left-sided knee joint disease, only one affected leg will succumb.
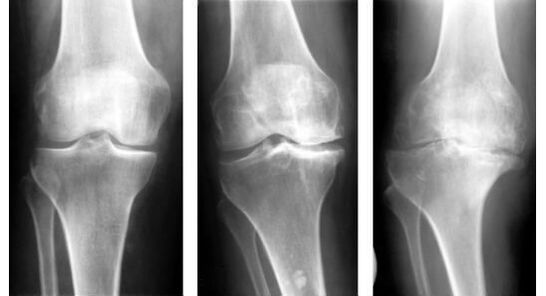
- Pathological manifestations of the first stage:While pain is not yet an issue, patients may notice rapid fatigue when performing sports or physical activity and slight limitations in joint range of motion after prolonged rest. An X-ray will show a slight narrowing of the space between the joint bones and an uneven surface of the cartilage with slight compaction.
- For 2nd degree knee arthrosisSymptoms appear more pronounced and more frequently. The patient is usually already aware that something is wrong with his knee. Joints can become injured and "twisted" due to changes in weather or physical activity. Even the slightest movement can cause knee pain. If a person lets the leg rest, the pain will go away. But under load they will recover again. Also at this stage of the pathology, there may be a characteristic tightness in the knee when bending and extending the leg, and difficulty and pain may occur when trying to bend the knee beyond 90 degrees. X-rays will show changes in the shape of the joint cup and the presence of fluid in the joint space.
- Knee arthritis 3rd degreeIt is characterized by severe pain that occurs regardless of whether the limb is under load or at rest. Painful joints are especially painful at night and when weather conditions change. The patient is no longer able to bend his leg at the knee, which is why his physical activity and performance decline. X-rays clearly show degenerative changes in joint tissue. The deformation is also obvious when observed with the naked eye. The patient's legs bend at the knees, forming an "o" or "x" shape, ultimately resulting in the inability to move independently without support and the inability to perform daily professional and household tasks. The person becomes disabled.
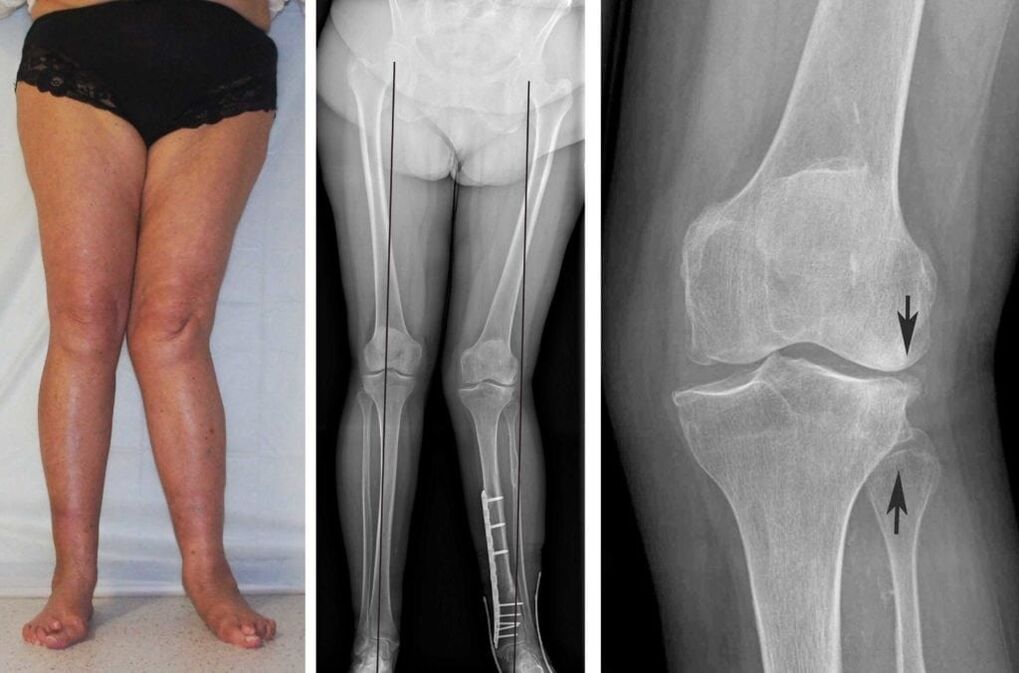
diagnosis method
- Enlargement and shape change of the knee joint;
- A noticeable crunching sound when the kneecap shifts;
- Pain when palpating the joint;
- Joint movement is limited.
Classification
- Primary knee arthropathy;
- Secondary knee arthropathy.
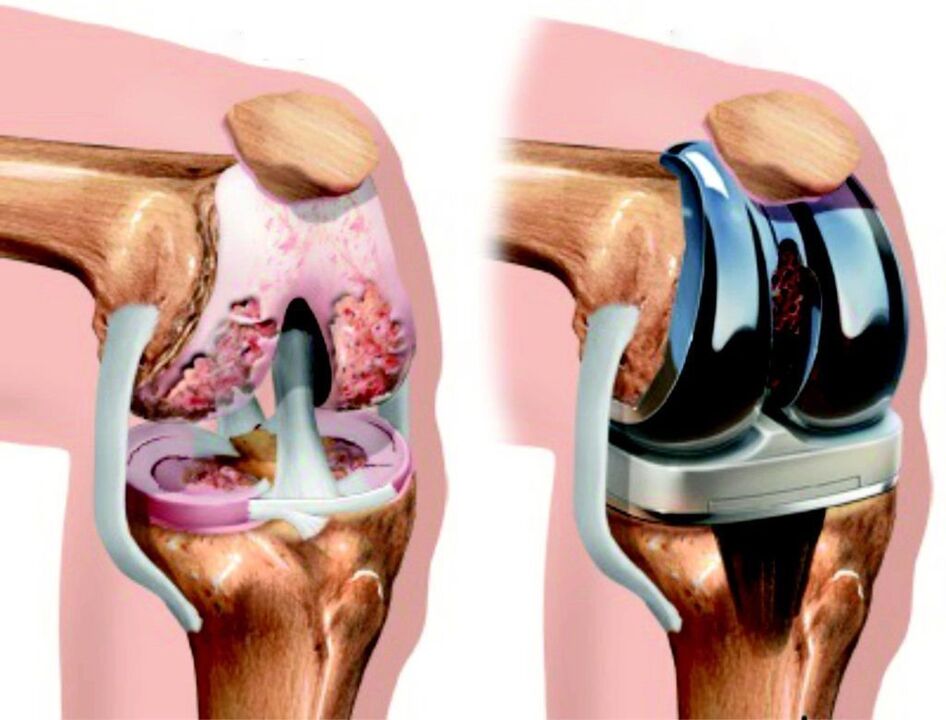
Official medicine for treating knee joint disease
- Relieve pain and discomfort;
- Restore joint mobility;
- Stop the destruction of the cartilage layer and, if possible, restore it.
Drug treatment of knee joint disease
- NSAIDs– Joint treatment begins with them, they quickly relieve pain, swelling, fever and partially stop the inflammatory process. But they cannot be taken for a long time, since the active ingredients in the composition have an extremely negative impact on the function of the digestive tract and blood components. Typically, NSAID treatment courses last no longer than 5-7 days. Medications may come in the form of tablets for internal use or ointments and gels for external use.
- chondroprotectant– These drugs improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue and restore its hardness and elasticity. Chondroprotectants may also provide partial relief from pain and swelling. But these drugs don't work immediately. The first effects will be visible within a few weeks of starting the treatment. It is recommended to take chondroprotectants for at least six months.
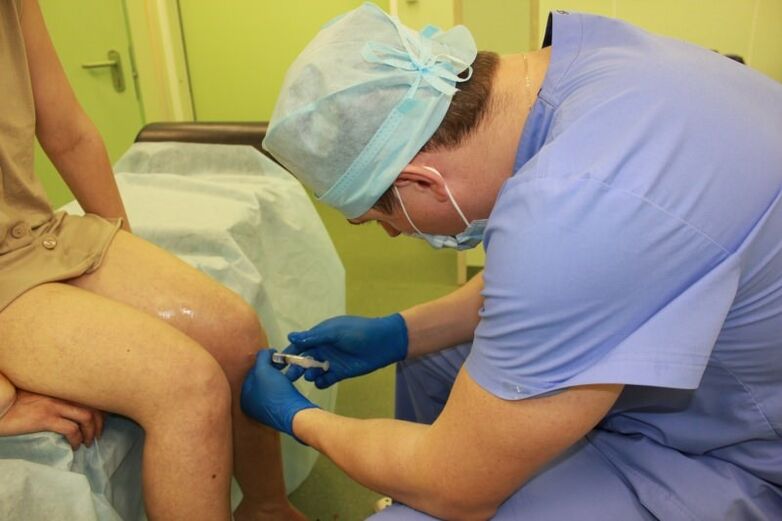
- Hormone drugs.They are also called corticosteroids. If the pain is very severe and inflammation continues to progress even after a course of NSAIDs, medications containing hormones may be used. They are administered via intramuscular injection or directly into the joint space. These medications provide immediate pain relief, reducing swelling and inflammation. But they have many contraindications and even more side effects than NSAIDs, which is why they are only used in extreme cases. Hormone drugs can only be purchased in pharmacies with a doctor's prescription. Once the patient's condition improved, corticosteroids were discontinued immediately.
Remark:Of all the drugs listed above, only chondroprotectants affect the cause of the disease. They stimulate the regeneration of damaged cartilage tissue and prevent damage to surviving cartilage cells. But these drugs are expensive and must be taken regularly for months, sometimes even years, to achieve significant and lasting effects. For many patients, especially pensioners, the cost of comprehensive treatment is often prohibitive.
Unconventional treatments
Treat with dandelion
- Collect exactly 50 open dandelion heads.
- Place in a dark glass bottle with a tight stopper.
- Pour in 300 ml of good quality vodka or triple cologne.
- Avoid sunlight for a month and shake the container occasionally.
- No need to express, transfer to the first aid kit, rub it on your sore knees before bed, then wrap the joints warmly, cover yourself with a blanket and go to bed.

Burdock Recipes
- Pick two to three young leaves and rinse them with cold water;
- Gently mash the leaves to release the juice;
- Apply to affected joint and immobilize with bandage.
Turpentine, Eggs, and Other Joint Remedies
- Lightly beat one egg yolk in a bowl.
- Add a small spoonful of turpentine and stir.
- Then pour in a tablespoon of vinegar and stir again.